Country Benefits
Sao Tome & Principe as the financial hub for the B Line will benefit as follows:
- Investment in Infrastructure: Funding agent of robust infrastructure projects for the continent, including transportation networks, power plants, and industrial zones, is crucial for supporting manufacturing activities. Improved infrastructure reduces production costs, facilitates the movement of goods and raw materials, and attracts investment in manufacturing facilities.
- Skills Development and Education: Investing in education and skills development programs focused on finance, science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields prepares the workforce for careers in manufacturing and technology. Providing vocational training and technical education equips individuals with the skills needed to operate modern manufacturing equipment and processes.
- Promotion of Research and Innovation: Encouraging research and innovation in manufacturing technologies and processes fosters the development of advanced manufacturing capabilities. Collaboration between universities, research institutions, and industry stakeholders can lead to the creation of innovative products, processes, and solutions tailored to local market needs.
- Regional Integration and Trade Agreements: Enhancing regional integration and trade agreements facilitates the movement of goods, services, and capital across borders, expanding market access for manufactured products. Harmonizing trade policies, reducing trade barriers, and promoting intra-regional trade can stimulate demand for locally manufactured components and electronics.
- Adoption of Industry 4.0 Technologies: Embracing digitalization, automation, and advanced manufacturing technologies under Industry 4.0 enables African countries to leapfrog traditional manufacturing models and compete globally. Leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, additive manufacturing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) enhances productivity, efficiency, and product quality in manufacturing operations.
Libya
There are 480 ports of various sizes in the Mediterranean and that around 40 percent of sub-Saharan trade passes through the Mediterranean. He said up to 40 percent of the cost of goods to some sub-Saharan states, especially the landlocked states, is made up from transport costs. This is a high ratio. Libya can deliver goods by train to its southern border at a much cheaper rate.
The transport expert pointed out that roads to Chad and Niger of varying quality already exist and that the law to build better quality roads to the south exists. It needs implementation. These roads would facilitate the building of the railway system to the south.
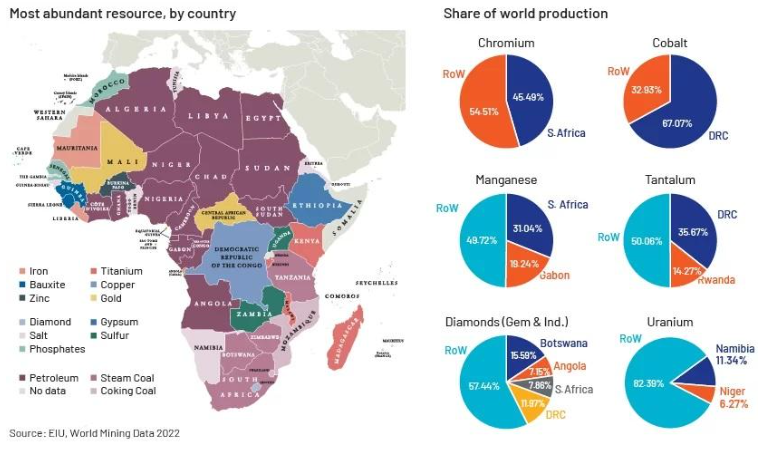
Countries with critical minerals & natural resources
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is renowned for its vast reserves of mineral resources, including copper, cobalt, diamond, oil, coltan, gold, and tin. These abundant natural deposits have made the DRC one of the most mineral-rich countries in Africa since its independence in 1960. However, the exploitation of these resources has been fraught with challenges, including issues of legality and governance. In 2010, the government took steps to address concerns about the illegal extraction and trade of minerals by suspending mining activities while investigations were conducted. Despite these challenges, the DRC remains attractive to foreign mining enterprises, with around twenty such companies operating in the country as of 2011. With its wealth of resources, including oil, copper, coltan, cobalt, gold, diamonds, and others, the DRC holds significant potential for economic development and investment in the mining sector.
Zambia stands out as the leading African country in copper production, boasting an undisputed status as the continent’s top copper producer and supplier. The nation’s Copperbelt region is renowned for its extensive copper production, with Zambia alone responsible for 77% of Africa’s total copper output. Notably, Zambia is home to the largest underground mine on the continent, employing approximately 10,000 workers and yielding an impressive annual copper production of around 300,000 tons. In addition to copper, Zambia also possesses significant deposits of other valuable minerals, including emerald and cobalt, further contributing to its status as a key player in the African mining industry.
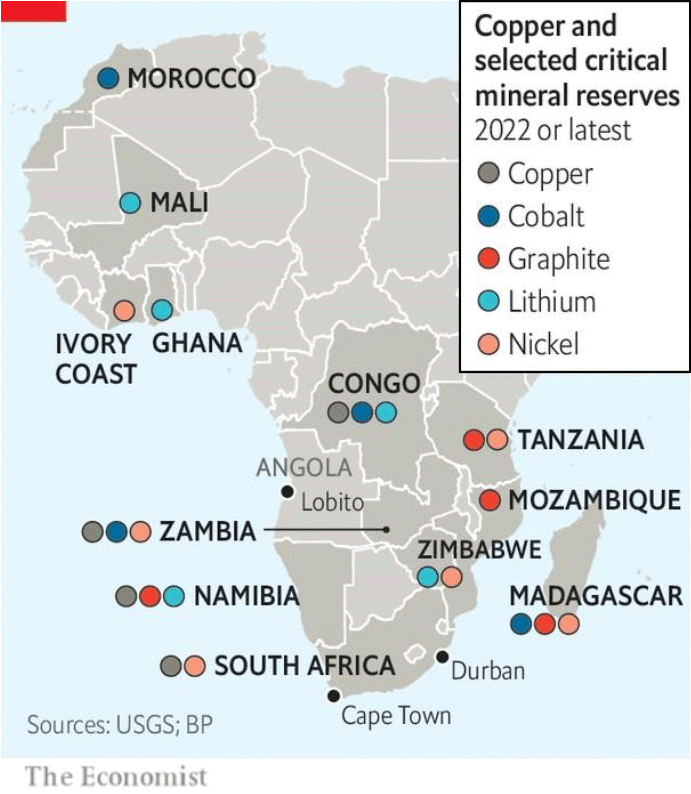
Tanzania boasts a diverse range of valuable minerals, including tanzanite, gold, diamonds, and silver, cementing its position as a significant player in the global gemstone and precious metal markets. As the exclusive source of tanzanite worldwide, Tanzania holds a unique position in the gemstone industry, further bolstered by its status as the fourth richest country in Africa in terms of gold production. Over the years, Tanzania’s gold mining sector has experienced fluctuations, but foreign investment in the country’s rich mineral resources has led to the establishment of numerous mining operations, contributing to economic growth and development. Alongside agriculture, the gold and tanzanite trade play a pivotal role in Tanzania’s economy, with mineral exports serving as a vital driver of economic prosperity.
Gabon occupies a strategic position in a region renowned for its abundance of mineral resources, which form the cornerstone of the country’s economy. Among its rich mineral reserves are manganese, diamonds, gold, and uranium, each playing a significant role in driving economic activity and development. The mining industry serves as the backbone of Gabon’s economy, with mineral extraction and processing activities driving growth and prosperity across various sectors. With its wealth of mineral resources, Gabon is well-positioned to capitalize on the opportunities presented by its natural endowments to foster sustainable economic development and prosperity.
South Africa is rich in diverse mineral resources, including gold, platinum, coal, diamonds, iron ore, manganese, and chromium. The country is a leading producer of precious metals and minerals, making it a key player in the global mining industry.
Botswana is known for its diamond reserves, which have propelled the country to become one of the world’s leading producers of gem-quality diamonds. Additionally, Botswana has significant deposits of coal, copper, nickel, and salt.
Namibia is renowned for its diamond production, with offshore diamond mining being a significant contributor to the country’s economy. Namibia also has deposits of uranium, zinc, lead, copper, and gold, as well as extensive marine resources along its coastline.
Angola is rich in oil and natural gas reserves, making it one of Africa’s top oil producers. The country also has substantial diamond deposits, as well as deposits of iron ore, copper, gold, and phosphates.
Zimbabwe has vast mineral resources, including gold, platinum, diamonds, coal, nickel, and lithium. The country has historically been a major producer of gold and diamonds, with significant potential for further development in other mineral sectors.
Mozambique is rich in natural resources, including coal, natural gas, titanium, tantalum, graphite, and gemstones. The country’s coal reserves are among the largest in the world, while its offshore natural gas deposits have attracted significant investment in recent years.